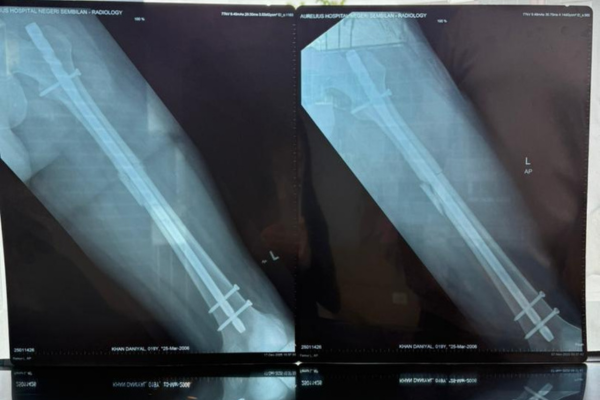
Femur Fracture (Post Surgery)
Fractures of the femur are relatively common injuries and are not typically amenable to nonoperative treatment. Early surgical fixation is recommended, for instance an Intramedullary nailing surgery.
Femoral Fracture Fixation Surgery: Intramedullary Nail (Cite from: Medical Legal Art)
Why Rehab?
Phase 1 physiotherapy (day 1 post op to day 14) :
– Foot flat weight bearing (Weight of leg on ground.) gait training with crutches
Isometric quadricep strengthening, VMO emphasis.
Progress to independent mobility as tolerated.
1st follow-up with your surgeon: day 14 post op
– XR of hip: Ap/ Lat hip. Confirm that fixation is stable, no evidence of loss of reduction or new injury.
Weightbearing: for Midshaft fracture, weight bearing as tolerate
2nd follow-up with your surgeon at 8 weeks after surgery.
– XR of hip: AP/ Lat views. Confirm that fixation is stable and fracture has healed radiographically
Phase 2 physiotherapy (week 8 – week 12 after surgery)
– Regain Ambulatory Status:
Wean from assistive devices as tolerated
Weight bearing training, step up, step down
3rd follow-up with your surgeon at 3 months:
– XR of femur: AP/Lat. Confirm union of fracture. If united, then this is the last x-ray.
Phase 3 physiotherapy (week 12 – week 16 after surgery)
Plyometrics training, return to sports regime
Treatment Approach
Rehabilitation week 1-week 3 post femur fracture.
Why knee stiffness is common after Intramedullary (IM) Nail Fixation:
– Entry point often through piriformis or trochanteric region.
– Quadriceps & patellar tendon irritation.
– More anterior knee pain.
– Soft tissues usually tolerate earlier motion.
ROM Expectations:
– Knee ROM is usually allowed early.
-Goal:
– 0–60° by week 1–2
– 90° by week 3–4
– Functional flexion by 6 weeks
– Muscle energy technique
– Hold relax technique
– Dry needling to reduce muscle tension
